250128 'ANAX' http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de/AEA_I.HTM or http://color.li.tu-berlin.de/AEA_I.HTM.
'ANAX':@PROZ_AEA_I.COM format: 'dmyy'LINKSEA_H.HTM
Go to this page in German AGA_I.HTM
Chapter A:
Colour Image Technology and Colour Management (2019)
Introduction, content list and summary:
AEAI,
AEA_I,
AEA_S in English or
AGAI,
AGA_I,
AGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
AEAS,
ae2s in English or
AGAS,
ag2s in German.
Chapter B:
Colour Vision and Colorimetry (2020)
Introduction, content list and summary:
BEAI,
BEA_I,
BEA_S in English or
BGAI,
BGA_I,
BGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
BEAS,
be2s in English or
BGAS,
bg2s in German.
Chapter C:
Colour Spaces, Colour Differences, and Line Elements (2021)
Introduction, content list and summary:
CEAI,
CEA_I,
CEA_S in English or
CGAI,
CGA_I,
CGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
CEAS,
ce2s in English or
CGAS,
cg2s in German.
Chapter D:
Colour Appearance, Elementary Colours, and Metrics (2022)
Introduction, content list and summary:
DEAI,
DEA_I,
DEA_S in English or
DGAI,
DGA_I,
DGA_S in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
DEAS,
de2s in English or
DGAS,
dg2s in German.
Chapter E:
Colour Metrics, Differences, and Appearance (2023)
Introduction, content list and summary:
eeai,
eea_i,
eea_s in English or
egai,
ega_i,
ega_s in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
eeas,
ee2s in English or
egas,
eg2s in German.
Chapter F:
Colour metrics for chromatic and luminance adaptation (2024)
Introduction and content list:
feai,
fea_i in English or
fgai (under work),
fga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
feas,
fe2s in English or
fgas,
fg2s in German.
Chapter G:
Equally spaced colour scales for optimal colour-image quality (2024b)
Content list:
gea_i in English or
gga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 and 260 image series:
geas
ge2s in English or
ggas,
gg2s in German.
Chapter H:
SDR and HDR-colour metric for optimal colour-image quality (2025)
Content list:
hea_i in English or
hga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 (and 260, under work) image series:
heas
he2s in English or
hgas,
hg2s in German.
Chapter I:
Output linearization of visual data for scaling and thresholds (2025b)
, under work
Content list:
iea_i in English or
iga_i in German.
Image pages with 10 (and 260, under work) image series:
ieas
ie2s in English or
igas,
ig2s in German.
Remarks:
Any large image file with 260 pages, for example
he2s.htm,
can be printed as image series.
Also the content can be saved as a pdf file for any of the chapters A to H.
In addition a download of the corresponding pdf file, for example
he2s.pdf (about 150MB) is possible.
Project title: Colour and colour vision with Ostwald, Device, and elementary colours -
Antagonistic colour-vision model TUBJND and properties for many applications
Chapter A: Colour Image Technology and Colour Management (2019),
Main part AEA_I
Each chapter includes main parts (I) with information to an image part (S).
There are 26 image parts (S), each with 10 figure pages.
The 10 figure pages (0 to 9) include up to 16 figures,
and each figure with up to six formats.
Structure, content, and order of files and figures on the example chapter
Colour Vision and Colorimetry
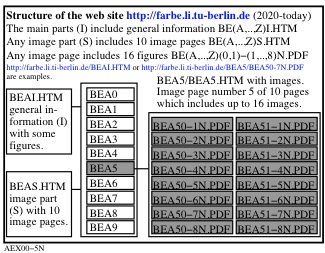
Figure 1 shows the structure of the web site BE(A..Z)I.HTM und BE(A..Z)S.HTM.
For the download of this figure in the VG-PDF format, see
AEX00-5N.PDF.
Structure, content, and order of files and figures on the web site
http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de.
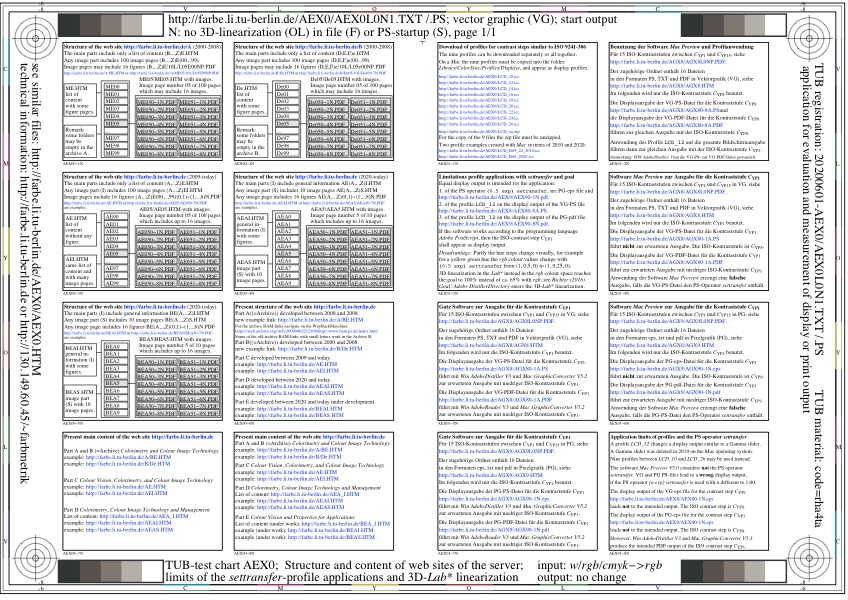
Figure 2 shows the structure, the content, and the order of files and figures on the web site
http://farbe.li.tu-berlin.de.
For the download of this figure in the VG-PDF format, see
AEX0L0N1.
List of links to the contents of all image parts
Image part AEAS
in English or AGAS in German.
Title: Colour management in the RGB*-colour space with the
ISO/IEC-test chart AE49 according to ISO 9241-306
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Change of colour spacing in hue planes by the luminance reflection
of the ambient light on the display surface.
3. PostScript program code for application of the 1-Minus-Relation
(1MR).
4. PostScript-Program code for production of 15 ISO-contrast steps.
5. Colour management with the Profile Connection Space (PCC) in Lab*
and RGB*.
6. ISO-colour file AE49 and the colour loop: ISO-file -> print -> scan ->
ISO-file
for many applictions.
7. Chromatic test chart AE49 with 1080 colours without and with the
1-Minus-Relation (1MR).
8. Chromatic test chart AE49 for 5 and 15 ISO-contrast steps.
9. Chromatic test chart AE49 with rgb, cmy0, and cmyk data.
for further information and discussion,
see AEAI.
go to the image part AEAS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEBS
in English or AGBS in German.
Title: Change of ISO/IEC-test charts according to ISO/IEC 15775
and ISO 9241-306 from vector to pixel graphic und production
of 15 ISO-contrast steps with PostScript
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Example for colour management in a virtual design room.
3. PostScript program code for the application of the
1-Minus-Relation (1MR).
4. PostScript program code for the production of 15 ISO-contrast
steps.
5. ISO/IEC-test charts according to ISO/IEC 15775 and ISO 9241-306.
6. Chromatic test chart for 1080 colours and colour code (row/column).
7. Achromatic test chart with elements for spacing, resolution, readability
and visibility.
8. Chromatic test charts with similar elements in colour.
9. Change of any achromatic and chromatic ISO-test chart from vector graphic
VG to pixel graphic PG.
10. Change of any PG file of the standard ISO-contrast step CYP8
to the 15 ISO-contrast steps with use of the PS operator
settransfer.
for further information and discussion,
see AEBI.
go to the image part AEBS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AECS
in English or AGCS in German.
Title: The technology of the ISO/IEC image with a flower motiv based on
a reflective original
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Analog original with a 16-step gray scale of equal spacing in L*,
and CIE-test colours.
3. Properties of the digital ISO/IEC image with photo-CD technology.
4. Properties of the digital ISO/IEC image for slide (sf) and negative film
(nf).
5. Properties between two stops under and over exposure.
6. Output linearization produces similar rgb* files
for allexposures.
7. Digital ISO/IEC image for five resolutions.
8. Digital ISO/IEC image in the formats rgb and cmy0.
for further information and discussion,
see AECI.
go to the image part AECS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEDS
in English or AGDS in German.
Title: Test charts similar to ISO 9241-306:2018 in vector graphic
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Original ISO/IEC-test charts for relative contrast gP=1,000
(CYP8).
3. Charts for 5 ISO-contrast steps gP=0,475, 0,775, 0,850, 1,000,
2,105
(CYP1, CYP5, CYP6, CYP8, CYP15)
with text.
4. Charts for 15 ISO-contrast steps 0,475<=gP<=2,105
(CYP1, ..., CYP15).
5. Charts are similar to the charts AE29, AE39, AE49, AE09, AE19 of
ISO 9241-306.
6. Applications are between low contrast (high luminance reflection of the
ambient light) and high contrast (low reflection) on the display
surface.
7. Modification of the ISO-contrast step CYP8 to CYP5
or office-work places.
for further information and discussion,
see AEDI.
go to the image part AEDS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEES
in English or AGES in German.
Title: Test charts similar to ISO 9241-306:2018 and linearized
ISO/IEC images
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Original ISO/IEC-test charts for the relative standard contrast
gP=1,000 (CYP8).
3. Charts for 5 ISO-contrast steps gP=0,475, 0,775, 0,850, 1,000,
2,105
(CYP1, CYP5, CYP6, CYP8, CYP15)
with text.
4. Charts for 15 ISO-contrast steps 0,475<=gP<=2,105
(CYP1, ..., CYP15).
5. Charts are similar to the charts AE59, AE18/28 (with ISO/IEC image)
of ISO 9241-306.
6. Applications are between low contrast (high luminance reflection of
the ambient light)
and high contrast (low reflection) on the display surface.
7. Modification of the ISO-contrast step CYP8 to CYP5
for office-work places.
8. Linearized ISO/IEC image of four ISO-contrast steps
(CYP1, CYP5, CYP8=CYN8
and CYP15=CYN1) with rgb and cmy0 data
of slide (sf) and negative film (nf).
for further information and discussion,
see AEEI.
go to the image part AEES
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEFS
in English or AGFS in German.
Title: Test charts similar to ISO 9241-306:2018 and linearized
ISO/IEC images
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Original ISO/IEC-test charts for the relative standard contrast
gP=1,000 (CYP8).
3. Charts for 5 ISO-contrast steps gP=0,475, 0,775, 0,850, 1,000,
2,105
(CYP1, CYP5, CYP6, CYP8, CYP15)
with text.
4. Charts for 15 ISO-contrast steps 0,475<=gP<=2,105
(CYP1, ..., CYP15).
5. Charts are similar to the charts AE39 of ISO 9241-306,
however with 16 and 32 instead of 20 hue steps.
6. Applications are between low contrast (high luminance reflection of
the ambient light)
and high contrast (low reflection) on the display surface.
7. Modification of the ISO-contrast step CYP8 to CYP5
for office-work places.
8. Test charts include Code (position row/column) of 16 and 32 hue steps
of the 1080 colours of the test chart AE49.
for further information and discussion,
see AEFI.
go to the image part AEFS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEGS
in English or AGGS in German.
Title: Hue circles; chroma or exponential transfer from rgb*
to rgb*i coordinates; standardization of the ISO-colour loop
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Transfer of rgb* to nicwde* coordinates.
3. CIELAB data of elementary hue circles of Miescher, offset OLS18
and display TLS18.
4. rgb* colours for six colours RYGCBM with transfer of the
relative chroma c*.
5. rgb* colours for six colours RYGCBM with exponential transfer
rgb*^n with the exponent n.
6. Affine ergonomic colour metric, standardization and properties of
Eigen (E) and opponent colours (O).
for further information and discussion,
see AEGI.
go to the image part AEGS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEHS
in English or AGHS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device sRGB,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data,
and ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5,
and 40,3,
and the adaptation to white YWa=88,6
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device sRGB;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, white adaptation YWa=88,6.
3. Eight sRGB-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YWa=88,6.
for further information and discussion,
see AEHI.
go to the image part AEHS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEIS
in English or AGIS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes
for the device WCGa (Wide Colour Gamut),
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to white YWa=88,6
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device WCGa;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, white adaptation YWa=88,6.
3. Eight WCGa-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YWa=88,6.
go to the image part AEIS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEJS
in English or AGJS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device Offs,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data,
and ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5,
and 40,3,
and the adaptation to white YWa=88,6
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device Offs;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, white adaptation YWa=88,6.
3. Eight Offs-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YWa=88,6.
go to the image part AEJS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEKS
in English or AGKS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device Ostw,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to white YWa=88,6
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device Ostw;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, white adaptation YWa=88,6.
3. Eight Ostw-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YWa=88,6.
go to the image part AEKS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AELS
in English or AGLS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device sRGB,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to grey YZa=18,0
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device sRGB;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, grey adaptation YZa=18,0.
3. Eight sRGB-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YZa=18,0.
go to the image part AELS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEMS
in English or AGMS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device WCGa
(Wide Colour Gamut),
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to grey YZa=18,0
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device WCGa;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, grey adaptation YZa=18,0.
3. Eight WCGa-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YZa=18,0.
go to the image part AEMS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AENS
in English or AGNS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device Offs,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to grey YZa=18,0
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device Offs;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, grey adaptation YZa=18,0.
3. Eight Offs-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YZa=18,0.
go to the image part AENS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEOS
in English or AGOS in German.
Title: Colour properties in six device-hue planes for the device Ostw,
with CIELAB-LabC*h and L*ABJND-L*ABCh output data, and
ambient-light reflections for black YN=0, YNn=2,5, and 40,3,
and the adaptation to grey YZa=18,0
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the device Ostw;
YN=0, YNn=2,5 and 40,3, grey adaptation YZa=18,0.
3. Eight Ostw-device colours RYGCBMNW
for eight ambient-light reflections according to ISO 9241-306;
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, CIELAB-LabC*h,
and L*ABJND-L*ABCh-output data for YZa=18,0.
go to the image part AEOS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEPS
in English or AGPS in German.
Title: sRGB, WCGa, Offs, and Ostw colours in six device-hue planes
WCGa and Offs colours in four elementary-hue planes,
and with CIELAB-LabC*h output data,
and the ambient-light reflections for black YN=0 and YNn=2,5,
and the adaptation to white YWa=88,6
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the devices sRGB, WCGa, Offs, and Ostw;
YN=0, YNn=2,5, and white adaptation YWa=88,6.
3. ISO-rgb* input and CIELAB-LabC*h output
for the devices WCGa and Offs colours in four elementary-hue planes
ISO-rgb*, CIE-XYZxy, and
CIELAB-LabC*h-output data for YWa=88,6.
4. Ostwald-hue circle with 16 steps;
Calculation of elementary colours according to CIE R1-57:2015
with relative hue scaling.
5. CIE data of eight Offset and BAM-test colours; Output in
six hue planes.
6. CIE data of the display system sRGB according to IEC 61966-2-1
(ITU-R BT.709.3) and of the display system WCGa (Wide Colour Gamut)
according to ITU-R BT.2020 for the white adaptations YWa=100,
and YWa=88,6.
go to the image part AEPS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEQS
in English or AGQS in German.
Title: ISO and CIE standard documents for achromatic colours,
Relation between colorimetry and physiological signals in colour vision,
Luminance and contrast discrimination as function of luminance,
CIE data of the continuous colour circle of Ostwald
with elementary colours
1. Introduction and goals.
2. ISO and CIE standard documents for achromatic colours.
3. Relation between colorimetry and physiological signals in colour vision.
4. Luminance and contrast discrimination as function of luminance.
5. CIE data and diagrams of the continuous colour circle of Ostwald
with elementary colours.
go to the image part AEQS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AERS
in English or AGRS in German.
Title: Four Ostwald and six special optimal colours;
CIEXYZ, CIELAB and LABJND in different tables and diagrams;
5 step offset and BAM-test colours in four hue planes
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Four Ostwald and six special optimal colours.
3. CIEXYZ, CIELAB and LABJND in different tables and diagrams.
4. 5step offset and BAM-test colours in four hue planes.
go to the image part AERS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AESS
in English or AGSS in German.
Title: Colour-valence metric and higher colour metric;
Equation for CIE tristimulues values and lightness;
Equations for chroma, chromatic value, and chromaticity;
Contrast steps and changes according to ISO 9241-306;
Six device and four elementary colours of the devices sRGB and Ostw
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Colour-valence metric and higher colour metric.
3. Equation for tristimulues values and lightness.
4. Equations for chroma, chromatic value, and chromaticity.
5. Contrast steps and changes according to ISO 9241-306.
6. Six device and four elementary colours of the devices
sRGB and Ostw (Ostwald).
go to the image part AESS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AETS
in English or AGTS in German.
Title: Achromatic and chromatic colour scaling;
Line elements of Stiles, Vos&Walraven, and
double line element of Richter;
Colorimetry and psycho-physical properties of colour vision;
Lightness, sensitivity and contrast according to CIELAB, LABJND,
and CIEDE2000;
Similar Weber-Fechner & Gauß functions for thresholds,
contrast and lightness;
Antagonistic model of colour vision based on optimal colours
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Achromatic and chromatic colour scaling.
3. Line elements of Stiles, Vos&Walraven, and
double line element of Richter.
4. Colorimetry and phychophysical properties of colour vision.
5. Lightness, sensitivity and contrast according to
CIELAB, LABJND, and CIEDE2000.
6. Similar Weber-Fechner & Gauß functions for thresholds,
contrast and lightness.
7. Antagonistic model of colour vision based on optimal colours.
go to the image part AETS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEUS
in English or AGUS in German.
Title: Hue circle of Ostwald-optimal colours;
YN=3,6, YW=90, for CIE standard illuminant D65 or illuminant
P60 (6000K);
XYZ, YABCh, YABCh1, and YABCh2 data;
Data for the CIE 02 and 10 degree observer in 8 colour diagrams;
Three elementary-colour systems;
Spectral properties of optimal and surface colours;
Space coordinates: device, optimal, and Arens colours
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Hue circle of Ostwald-optimal colours;
2.1 YN=3,6, YW=90, CIE standard illuminants D65, CIE 02 degree
observer;
XYZ data and 8 colour diagrams;
Data YABCh, YABCh1 and YABCh2 as table with wavelength
2.2 similar for CIE standard illuminant D65, CIE 10 degree observer;
2.3 similar for CIE illuminants P60 (6000K), CIE 02 degree observer;
3. Three elementary-colour systems
Spectral properties of optimal and surface colours;
Space coordinates: device, optimal, and Arens colours.
go to the image part AEUS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEVS
in English or AGVS in German.
Title: Ostwald-optimal colours;
YN=3,6, YW=90, for eight illuminants Dxx or Pxx;
XYZ, YABCh, YABCh1, and YABCh2 data;
Data for the CIE 02 and 10 degree observer in 8 colour diagrams;
Chromatic adaptation model for 8 Planck radiations
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Ostwald-optimal colours;
2.1 YN=3,6, YW=90, 8 illuminants Dxx, CIE 02 degree observer;
XYZ data and 8 colour diagrams;
Data YABCh, YABCh1 and YABCh2 as table with wavelength;
2.2 similar for 8 illuminants Dxx, CIE 10 degree observer;
2.3 similar for 8 illuminants Pxx, CIE 02 degree observer;
3. Chromatic adaptation model
Ostwald-optimal colours for 8 Planck radiations Pxx with
8 correlated colour temperatures between 6000K (P60) and 2500K (P25).
go to the image part AEVS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEWS
in English or AGWS in German.
Title: Technology for a gamma change of image files
of the standard size A4L with PostScript
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Step recognition for changes of the illumination and viewing angles
and mirror reflection.
3. Test chart for the dark room with the ISO-contrast step CYP8.
4. Test chart for the standard office with the ISO-contrast step
CYP5.
5. Test chart for the standard office with 15 ISO-contrast steps
CYP1 to CYP15.
6. Frame file in VG and ISO-AE49 file in VG.
7. Frame file in VG and ISO-AE49 file in PG.
8. Whole frame file and ISO-AE49 file in PG.
for further information and discussion,
see AEWI.
go to the image part AEWS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEXS
in English or AGXS in German.
Title: Technology for a gamma change of image files with profiles
and PostScript
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Content, structure and names of many web pages and figures.
3. Gamma calibration with Mac OS V10.7.5 and display output
of 1080 colours.
4. 1080 standard colours at 16 standard positions similar to ISO 9241-306:AE49
for up to 15 ISO-contrast steps CYP1 to CYP15.
5. Creation of colour profiles with Mac OS V10.7.5 and use
on computers.
for further information and discussion,
see AEXI.
go to the image part AEXS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEYS
in English or AGYS in German.
Title: Technology for a change of vector to pixel graphic, input-output
relationships, and CIELAB-chroma and rgb values
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Different numbering for frame files and figure files in VG and PG.
3. Input-output relationship between CIE lightness L* and
8bit rgb data for slide film (sf) and negative film (nf)
between under and over exposure.
4. Device and elementary hue circles, and the location of LMS cones
in the hue circle, and chromatic and chroma data.
5. Device and elementary colours in the CIELAB-chroma diagram
(a*, b*).
6. Display output for 3x8 standard device systems, for example eight
Television Luminous System TLS00a to TLS70a according to ISO 9241-306.
7. Figures and eight tables with CIELAB chroma and rgb data
for 3 x 8 standard device systems.
8. User-output steering with rgb data on displays and by a transfer of
rgb to cmyk data for printers.
for further information and discussion,
see AEYI.
go to the image part AEYS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
Image part AEZS
in English or AGZS in German.
Title: Technology to change vector to pixel graphic and to mix both
1. Introduction and goals.
2. Different numbering for frame and figure files in VG and PG.
3. Change of file AE49 in small size in vector graphic for relative gamma
0,475 <= gP <= 2,105.
4. Change of file AE49 in small size to pixel graphic for relative gamma
0,475 <= gP <= 2,105.
5. Output of file AE49 in standard size with vector graphic for relative gamma
gP = 1,000.
6. Change of file AE49 in standard size to pixel graphic for relative gamma
gP = 1,000.
7. Change of 17 simple rectangle files from vector to pixel graphic
and mixture.
8. Change of 2 simple rectangle files from vector to pixel graphic
and mixture.
for further information and discussion,
see AEZI.
go to the image part AEZS
to study the 10 image pages and the content.
-------
For the start TUB web site (not archive), see
index.html in English,
indexDE.html in German.
For the archive information (2000-2009) of the BAM server
"www.ps.bam.de" (2000-2018)
about colour test charts, colorimetric calculations,
standards, and publications, see
indexAE.html in English,
indexAG.html in German.